What is Ethereum and How it Works?Total Review

Today we are going to talk about Ethereum. Many people associate Ethereum with Bitcoin and some people use the words Ethereum, Bitcoin and blockchain interchangeably by the end of this article you will know the key differences between Ethereum and Bitcoin and their relationship with the blockchain technology, specifically we will discuss what Ethereum is, what Ether is, how they work and what the future holds for this blockchain project.
I’ve divided this guide about Ethereum into seven chapters to make it simple and easy to follow
Chapter 1
What is a Ethereum?
Vitalik butyrin is a Russian Canadian programmer and cryptocurrency researcher who came up with the idea for Ethereum in 2013 which finally went live in 2015. The most plain and simple explanation of Ethereum can be broken down into two words: Software Platform.
What makes a Ethereum different from other software platforms?
It’s a blockchain based software platform.
What is blockchain?
The most plain and simple explanation of blockchain is that it is records of data stored on networks of computers and there are three pillars of blockchain that make it unique.
Decentralization.
Transparency and
Immutability.
Let’s break down these three pillars.
-
Decentralization
The word decentralization with regard to blockchain is two fold
one it means the data is recorded and stored on multiple devices in multiple locations around the world as opposed to one central place and
two decentralization also means that no one person, company, government authority or entity controls the data record and storage process.
So instead of traditional centralized entities like the IRS, JP Morgan or MIT, recording story, managing and controlling their data by following their own protocols, deciding which servers to use, where the servers are located and using their own proprietary software and security systems to protect their data.
Blockchain allows for decentralized record-keeping where data is recorded stored and managed on a network of computers with open source software around the world. Any changes to the blockchain protocol go through a consensus process that no one person or entity has control over. so that is the essence of the decentralization.
-
Transparency
The word transparency with regard to blockchain relates to the way in which transactions are recorded on a ledger, that is available for everyone to see and that is saved on a network of computers around the world making the data impossible to change or alter.
The best way to see the value of transparency and data recording storage and management is by comparing these two scenarios.
Currently common citizens of the United States are not privy to where and how every single tax dollar is spent by the United States government. We just have to take the government’s word for it and even if the government had to show their records it would be very easy for them to create Forge or manipulate any data they chose to share with us, since they control their own data.
You can see how that scenario is not transparent and not exactly trustworthy.
So let’s imagine if everyone in the United States had the ability to see alive running ledger of where every single tax dollar was spent by the United States government at any moment in time. Basically all US citizens could see a full disclosure of how our government is managing our money and in this scenario there is more trust and transparency. The second pillar of blockchain technology.
Also Read:Bitcoin Profit Review 2020 – Scam or legit? Complete Analysis
-
Immutability
Immutability simply means that the data recorded and stored on the blockchain cannot be changed forged or altered and this is achieved through cryptography and blockchain hashing processes.
To summarize the three pillars of blockchain technology.
Blockchains recording and storage protocols make it such that once new data is verified, it can’t be modified. It’s distributed across a vast network of computers around the world so it’s hard to destroy and no one person or entity controls the data or network, creating a completely transparent environment.
Now that you’re familiar with some of blockchains important features let’s talk about
The role blockchain plays in Bitcoin and Ethereum.
Bitcoin and Ethereum are both use cases of blockchain technology with different purposes.
Bitcoin is simply a digital currency that people can use as a form of payment to send to and from each other or hold as a store of value while
Ethereum is basically a programmable blockchain that people can build software on, to create valuable products and services or just for fun and due to the decentralized properties of blockchain technology, the software people can build on Ethereum are called- Decentralized Apps or DAPPS for short. The nature and potential of these decentralized applications or DAPPS has inspired the idea and desire for a crusade towards decentralized finance or DeFi for short.
The DeFi movement aims to transform the current financial system into a more transparent and trustworthy system like I described in the scenario we discussed in the transparency blockchain pillar segment.
So how is Ethereum’s blockchain based software application able to operate, if it’s not owned or controlled by a central entity or authority. The answer to that question leads us to chapter 2
Chapter 2
What is Ether?
Many people commonly use the words Ether and Ethereum interchangeably when they are actually two different things.
Ether is the ethereum blockchains native cryptocurrency. It operates similarly to Bitcoin. It’s a digital currency that can be transferred to people around the world, used as a form of payment or act as a store of value. However ether was created for an entirely different purpose.
Why does Ether exist?
If Bitcoin is digital gold ether could be described as digital oil. Ether was designed with the intention of fuelling the ethereum Network. Going back to the decentralized pillar of blockchain technology we discussed how open source software is distributed across a vast network of computers around the world to incentivize people to host in main.
The data on the block chain ether was created as a form of payment to fuel the etherium network so anyone who wants to build a software application on the Ethereum network has to pay for the computing power and space required using ether. The amount of Ether required for network fees is determined by a built-in pricing system known as GAS. Two other key differences between Bitcoin and Ether is that
Bitcoin has a fixed supply and halving events while ether currently does not. A fixed supply and halving events protect cryptocurrencies from inflation and a cap on the supply of ether may or may not be implemented in the future. We shall see what the future holds now let’s talk about how ethereum network fees are calculated.
Chapter 3
What is GAS?
GAS considers the bandwidth and space requirements as well as the computational difficulty of each transaction to calculate the amount of fees it will take to complete the term. GAS was created to differentiate the cost of performing transactions on the ethereum network from the actual value of the ether currency. So when executing transactions on Ethereum you will see GAS prices denoted in GWEI which stands for Giga way.
Giga wai (which is also referred to as nano ether or just nano) simply represents a fraction of ether to the 9th power. You can think of Giga ways to ether as penny’s to the US dollar similar to how US dollars have Penny’s, Nickels, Dimes and Quarters that represent fractions of one US dollar. Ether has multiple denominations of fractional values, the smallest denomination being WEI . Here’s a chart showing all of the different denominations of ether.
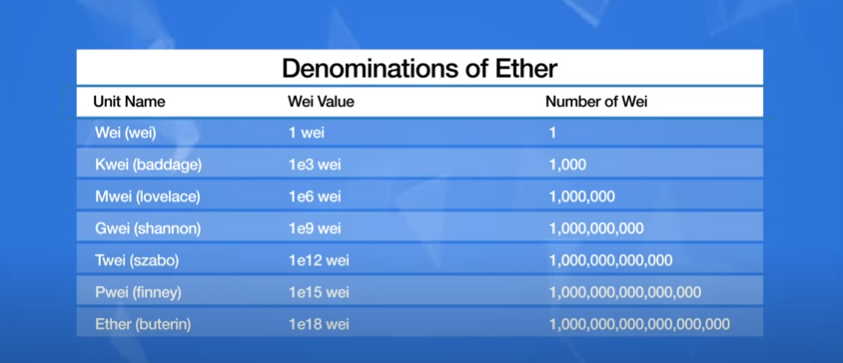
So if we look at one Giga wai of ether it’s depicted as a decimal point followed by 8 zeros and a one in the ninth place(1GWEI=0.000000001) you can see how it would be difficult to determine the amount of ether transactions will cost with all of the decimal places to keep track of instead of the GAS price for a transaction being.
Let’s say 0.000000003Ether, you can simply say 3 Giga wai and since the most common unit of ether reflected in GAS prices is Giga wai, that’s what denomination of ether is used to represent GAS prices. So when initiating a transaction on the Ethereum network you will see what’s called a GAS limit. In this field you can choose to increase or decrease the amount of ether you are willing to spend to complete the transaction. The higher the gas price the faster the transaction will be processed and if there’s not enough ether to complete the transaction you desire, you will receive an insufficient funds for GAS notification or similar.
Currently network processes on ethereum are completed by miners via a proof-of-work protocol which involves performing computational work on computer hardware to complete transactions. and miners which are actually called nodes are simply computers with software installed on them that connects them to the ethereum network. Then using computing power, they process and validate transactions in exchange for ether.
So using the built in GAS system miners or nodes are able to set minimum amounts of gas prices they are willing to accept to process transactions and if you don’t have enough Ether to cover the gas costs then no miners will perform the computational work required to complete the transaction.
Now when you use Ethereum, you will understand the difference between Ether and GAS as well as the reason why GAS prices are denoted in Giga wai and now that we have a basic concept of what Ethereum is and the roles Ether and GAS play in the network. Let’s get into more detail about how the Ethereum software platform works.
Chapter 4

How the Ethereum network works?
Let’s break down the Ethereum network into three simple layers so that we can understand how it works in a nutshell conceptually. Imagine the base layer of Ethereum consists of a vast network of computers called nodes. These Nodes are connected to the internet with software installed on them that runs the Etherium blockchain and this base layer of nodes is where transaction data is processed, validated, broadcasted and stored and as these Nodes perform the computational work required to process transaction data, they are rewarded with ether dictated by the GAS prices we discussed earlier.
These rewards incentivized nodes to maintain the Ethereum network by processing transaction data. Transaction data can contain value in the form of Ether and information in the form of Code. These codes can transmit data and trigger actions in the next layer of the Ethereum network. So imagine another layer on top of the Base Hardware Layer as a Software Layer. This software layer supports a programming language library that consists of languages like solidity, viper, bamboo and more. Using these computer languages developers can write, what are called smart contracts.
The term smart contract was actually coined back in 1998 by an American computer scientist named Nick Szabo who invented the digital currency bit gold ten years before Bitcoin was created. Szabo’s idea was to basically use computer code to execute terms of sophisticated contracts in the buying and selling of securities like options and futures, so smart contracts are just lines of code that dictate the terms of a contract and control the execution of the contract and with the nature of Ethereums Hardware layer and its blockchain based software. This creates the perfect trust worthy digital environment for building and executing smart contracts. Read more about auto trading app here
Smart contracts have the unique ability to authorize transactions and carry out terms of contracts within a trusted environment which eliminates the need for a central authority like a government bank or a legal system, so smart contracts make transactions Trackable, Transparent and Awesome. so we have the hardware layer in the software layer of Ethereum which combined basically creates a global decentralized supercomputer known as the Etherium Virtual Machine or EVM.
In computing virtual machines or VMS are simulations of computer networks that can be used for many different cases. In the case of the ethereum virtual machine or EVM a very basic and general idea of its role in the ecosystem is to improve the flexibility of the software and ensure separation of each software hosts in each software application. Software applications bring us to the final layer of Ethereum.
The application layer is where developers can build and launch third party decentralized applications or apps for short. These applications are decentralized because they operate on ethereum decentralized blockchain based platform. Popular examples of DAPS that have been created are crypto kitties which is a game and Augur which is a prediction market platform. At the time of this publication a total of 2772 DAPS have been launched on the Ethereum network, of which around 1500 are live. There are several different DAPPS categories including Games, Exchanges, Identity, Health, Property and much more. At the time of this publication the categories with the most transactions are games and exchanges while the categories with the most active users are finance and exchanges if you want to check out all of the current apps out there you can go to https://stateofthedapps.com and filter by the ethereum platform. Now another popular element of the ethereum ecosystem and apps brings us to the next chapter.
Chapter 5

What are ERC-20 Tokens?
Before we talk about ERC 20, let’s talk about what ERC means.
ERC is simply an acronym that stands for Ethereum Requests for Comments and it is similar to BIP which stands for Bitcoin Improvement Proposal. Since Ethereum and Bitcoin are blockchain based technologies, there is no one person or entity in charge of deciding, what new features to add, changes to make or fixes to implement to the protocols.
ERC is a process that was created as a way for people to contribute information about Ethereum or introduced features to the Ethereum Network. ERC’s or Ethereum requests for comments are basically how developers can propose improvements to the network so the number 20 of ERC 20 represents the unique ID number of that particular proposal so let’s talk about what ERC 20 is all about.
The ERC 20 is a token standard which is simply a list of rules that any tokens issued on the Ethereum block chain must follow.
What are tokens in the context of Ethereum?
Tokens are types of cryptocurrencies with different functions that represent an asset or are intended for specific use that operate on the Ethereum Blockchain, so the Ethereum ecosystem allows for the creation, deployment and circulation of virtual currencies or tokens.
ERC 20 proposed the implementation of rules and regulations developers must follow on creating tokens to issue on the Ethereum network. These rules can dictate how the tokens can be transferred transaction approval methods user access to the tokens in the total supply or number of tokens available, so ERC 20 basically ensures compatibility of new tokens issued on the etherium network.
Tokens that currently run on the Ethereum blockchain are referred to as GRC 20 tokens. Currently over 242,000 different tokens have been issued on the Ethereum network. Some of them are popular ERC 20 tokens include Tether, ChainLink, Vchain, and BAT. Each token has a different function or utility for example tether is a Token that is tethered to the US dollar in that it maintains the same value as the US dollar. This makes the token price stable staying at $1 per tether which is why tokens with this function are called stable coins.
Stable coins were designed to bridge the gap between fiat currencies and crypto currencies by allowing people with the token to hold an amount of cryptocurrency with a stable value. For example when you look at a crypto currency exchange you can see how Bitcoin and Ethereum prices are constantly in flux. One minute Bitcoin can be worth 10,300 and the next it can be worth 9600 with Tether, you can hold $10,000 of the token and minutes a minute and day by day, the value will remain unchanged which gives the token a lot of utility. An example of another token with different utility is BAT.
BAT stands for basic attention coin and it was created to be used as the currency for a web browsing DAPP called brave. BAT was designed as a form of payment to be traded between users, advertisers and publishers in exchange for user’s attention to advertisements and content creation. Another popular utility of tokens has been to raise capital to finance cryptocurrency projects which brings us to our next chapter
Chapter 6

What are ICO?
ICO stands for initial coin offering which operates similarly to an IPO or initial public offering. An initial public offering refers to when a privately held company decides to offer shares of their company to the public in the form of stock, on the stock market.
An initial coin offering is the cryptocurrency world’s application of this process by issuing tokens that are similar to stocks that sometimes depending on the utility of the token, have a function within the product or the service. ICO are used to raise capital through crowd funding in order to build a product or service typically a start up company wants to bring to market.
In fact Ethereum raised 18 million dollars worth of funds in only 42 days from conducting an ICO back in 2014 at that time ether was worth about 30 cents per ether. Now at the time of this publication ether is worth around 270 dollars so while ICO can be a great way for companies looking to build and offer blockchain based products and services to secure funding.
Investing in ICO is extremely risky since there is no regulation of the ICO process. Many investors risk losing any funds, they allocate towards ICO due to fraudulent projects, scams, legitimate projects being shut down for one reason or another or legitimate projects failing many times. An ICO raises, so much capital that the team loses any incentive to go through with the project and instead decides to take the money and abandon the project altogether. For that reason I do not highly recommend investing in ICO’s until more regulations have been implemented, that protect investors interests. Now that we are familiar with the ICO process GRC 20 tokens and how the ethereum ecosystem works conceptually, let’s take a look at what the future holds for this blockchain project.
Chapter 7
Ethereum 2.0
Later this year Ethereum will start to undergo a major Network update. It has been nicknamed the Ethereum 2.0, ETH and Serenity.
Ethereum 2.0 is the final iteration of the ethereum networks evolution and is set to launch later this year in 2020, which will coincidentally be a few months after the Bitcoin halving event. If everything stays on schedule this update will involve switching from miners processing transactions through proof of work protocols to validators processing transactions through what is called proof of State in addition. The update will feature sharding a new virtual machine and much much more. One of the main goals of this update is to improve the etherium networks efficiency and ability to scale.
Ethereum 2.0 will allow the platform to handle the growing demand for DAPPs and the DeFi movement at large. There are many phases to this massive upgrade so if everything stays on schedule it will be a few years until the upgrade is 100% implemented and complete. We will breakdown the phases of the Ethereum 2.0 upgrade and get into more of the conceptual and technical details in another article.













